Effective February 1, 2024, Google will implement new email sender guidelines for bulk senders, those who send more than 5,000 messages per day to Gmail inboxes. These guidelines aim to further enhance email deliverability, improve recipient engagement, and promote responsible sending practices.
Understanding and following these guidelines is important for both individuals and businesses to send emails that people will read and to keep a good sender reputation.
Guidelines what you must follow
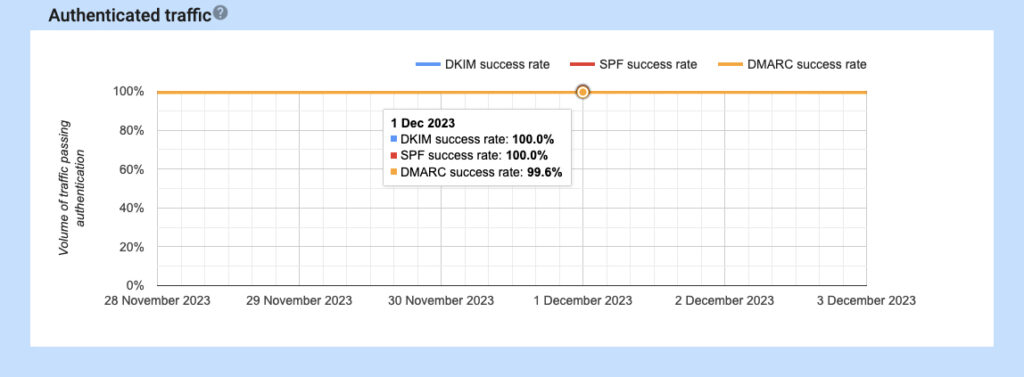
Authentication
- Set up email authentication using methods like SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) to show you’re the real sender and prevent impersonation.
- SPF records list the servers authorized to send emails from your domain, while DKIM digitally signs emails to prove they haven’t been tampered with.
- Consider adding ARC (Authenticated Received Chain) to enhance email authentication and track intermediate mail servers.
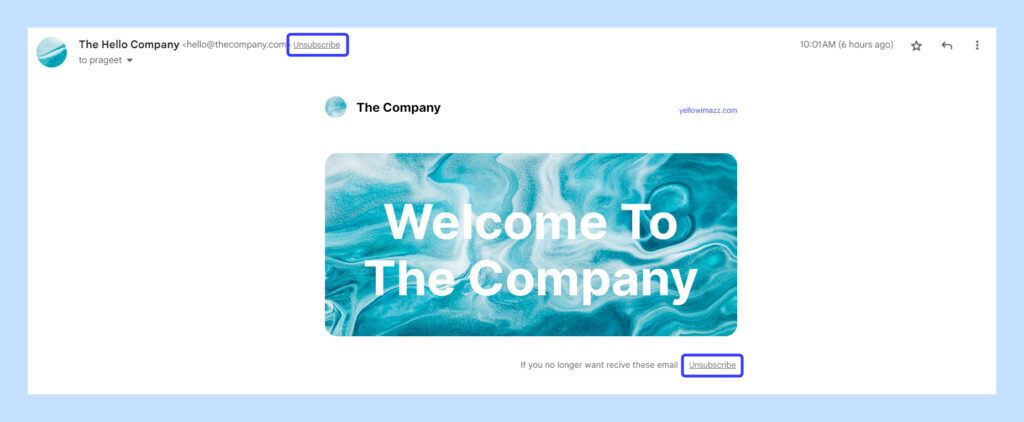
Opt-in and unsubscribe
- Respect recipient preferences by obtaining explicit consent (opt-in) before adding them to email lists.
- Provide clear and easy unsubscribe options in every email, allowing recipients to opt-out at any time.
- Honor unsubscribe requests promptly to maintain trust and avoid potential legal repercussions.
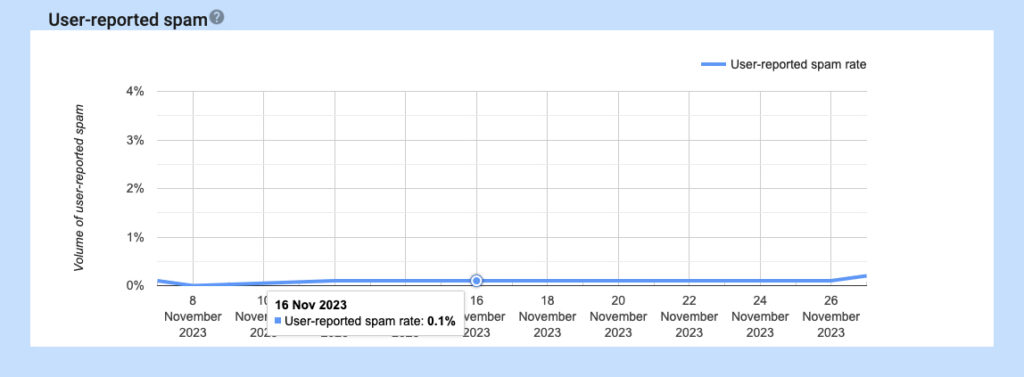
Content quality
- Prioritize high-quality, relevant, and engaging content that aligns with recipient expectations.
- Avoid hiding content in your messages using HTML and CSS. Messages may be flagged as spam if the content is hidden.
- Provide clear value to recipients to encourage engagement and reduce the likelihood of being marked as spam.
- Keep spam rates reported in Postmaster Tools below 0.3%.
- Format messages according to the Internet Message Format standard (RFC 5322).
Sending frequency
- Monitor sending volume and frequency to avoid overwhelming recipients and maintain a healthy balance.
- Sudden spikes in email volume can raise spam filters, so gradually increase sending volume over time.
- Segment your audience and tailor your sending frequency to each segment’s preferences.
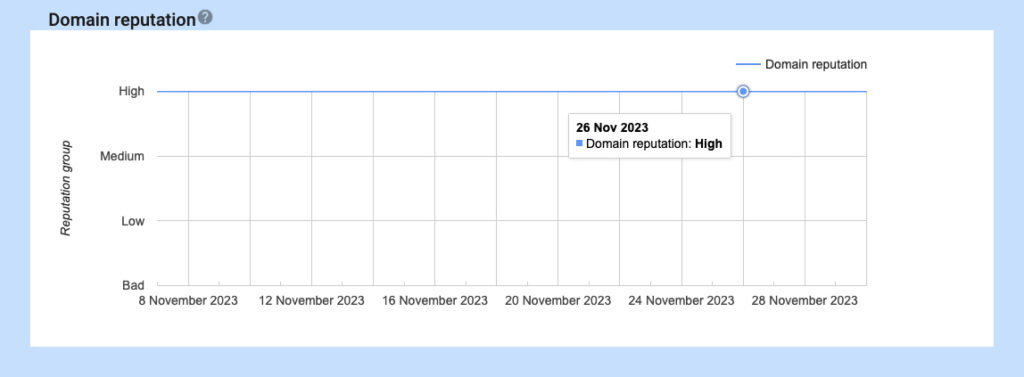
Domain reputation
- Regularly monitor your domain’s reputation using tools like Postmaster Tools to identify and address any potential issues that could impact email deliverability.
- Factors that can negatively impact domain reputation include high spam rates, invalid sender information, and poor unsubscribe practices.
- Take proactive measures to address any issues and maintain a positive domain reputation.
Shared IP responsibility
- If using a shared IP address, ensure the reputation of that IP is maintained by other senders using the same address.
- Communicate with other senders using the shared IP to ensure compliance with sender guidelines and maintain a positive reputation for all users.
- Consider using a dedicated IP address for high-volume or sensitive email campaigns.
Compliance with regulations
- Adhere to all applicable data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, to protect recipient information and maintain trust.
- Obtain explicit consent for data collection and usage, provide clear privacy policies, and enable individuals to access, modify, or delete their data upon request.
- Stay informed about evolving privacy regulations and adapt your practices accordingly.
Continuous monitoring
- Continuously monitor email performance metrics, including open rates, click-through rates, bounce rates, and spam complaints, to make data-driven improvements.
- Use analytics tools to identify trends and patterns in recipient behavior and tailor your email strategies accordingly.
- Regularly review and refine your email practices based on performance data and recipient feedback.
Keep in mind
The IP addresses you use for sending emails have valid PTR records. PTR records are a type of DNS record that maps an IP address to a domain name. This helps to establish the legitimacy of the sending IP address and can improve email deliverability.
Some additional tips for enhancing your email deliverability
Segment your audience: Tailor your email content to specific recipient segments based on interests, demographics, or behavior patterns.
Personalize your messages: Address recipients by name and personalize content to enhance engagement and relevance.
Optimize for mobile devices: Ensure your emails display correctly on mobile devices to cater to the growing mobile user base.
Utilize email marketing automation: Automate repetitive tasks, such as welcome emails and drip campaigns, to streamline your email marketing efforts.
Seek feedback and adapt: Encourage feedback from recipients to understand their preferences and make adjustments to your email strategies accordingly.




